JUNBO GE
December 1, 2022FDA Cleared Imbio an AI programs for scanning lung diseases; Neuromuscular Tongue Stimulator for Snoring & Vitls Platform for Remote Patient Monitoring
December 1, 2022Top AI in Pharma & Healthcare in 2022
The FDA approved apps to improve mental health, scan for diabetic retinopathy and develop drugs more efficiently with AI, to name a few...
App Uses AI Chats to Provide Mental Health Support
Youper is a unique artificial intelligence-powered mental health aide that enables discreet, caring, sympathetic interactions and mindfulness exercises. A chatbot offers users several coping mechanisms to assist them in resolving interpersonal difficulties throughout the deals. This chatbot was designed to help users process their feelings and use science-based psychological techniques in response. This simple software may be an extra tool in professional mental health counseling. Youper’s co-founder, a psychiatrist, Dr. Jose Hamilton from San Francisco, was inspired to create Youper when he observed the many barriers that kept his patients from seeking mental health care earlier, even if they had experienced symptoms for years.

Youper works a bit differently; It offers a personalized background and helps users evaluate particular emotions, including the underlying sources of those sentiments and specific psychological techniques that promote mental healing. The app may also prompt users to journal their thoughts and feelings to understand the problem better. Studies show that using artificial intelligence for mental health treatment can have promising results. In a 2017 Stanford University study of students experiencing depression, researchers found that those using an AI mental health app experienced a nearly 20% improvement in depressive symptoms in just two weeks. Researchers pointed out that their success was partly due to high levels of engagement through the app. According to Youper, 80% of users report a drop in negative moods after one conversation with the chatbot.(1)
Youper is a unique artificial intelligence-powered mental health aide that enables discreet, caring, sympathetic interactions and mindfulness exercises. A chatbot offers users several coping mechanisms to assist them in resolving interpersonal difficulties throughout the deals. This chatbot was designed to help users process their feelings and use science-based psychological techniques in response.

This simple software may be an extra tool in professional mental health counseling. Youper’s co-founder, a psychiatrist, Dr. Jose Hamilton from San Francisco, was inspired to create Youper when he observed the many barriers that kept his patients from seeking mental health care earlier, even if they had experienced symptoms for years. Youper works a bit differently; It offers a personalized background and helps users evaluate particular emotions, including the underlying sources of those sentiments and specific psychological techniques that promote mental healing. The app may also prompt users to journal their thoughts and feelings to understand the problem better. Studies show that using artificial intelligence for mental health treatment can have promising results. In a 2017 Stanford University study of students experiencing depression, researchers found that those using an AI mental health app experienced a nearly 20% improvement in depressive symptoms in just two weeks. Researchers pointed out that their success was partly due to high levels of engagement through the app. According to Youper, 80% of users report a drop in negative moods after one conversation with the chatbot.(1)
Atomwise: AI for drug discovery
Atomwise, a startup using AI to accelerate drug discovery has secured $123 million in funding this year. It will allow the startup to scale its technology and team as it expands its portfolio of collective experiences with researchers at the University of Toronto, Duke University School of Medicine, and others. Nowadays, fewer than 12% of all drugs entering clinical trials end up in pharmacies. Medicines take at least ten or more years to conclude the journey from discovery to the marketplace. According to the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, clinical trials alone take six to seven years, costing production roughly $2.6 billion. Atomwise claims its AtomNet platform can filter 16 billion chemical compounds for probable hits in under two days, expediting a process that typically takes months or years.
AtomNet’s AI algorithms screen for strength and the degree to which a pharmaceutical drug acts on a given site while protecting against toxicity, and they work on marks in hard-to-reach parts of the body. In one instance, Atomwise claims it was able to inhibit a protein-protein interaction in the nervous system for a multiple sclerosis project, exploring 8.2 million molecules that were useful in animal trials and have been approved by a pharmaceutical corporation in the UK. In another, the company found a drug candidate with no previous antiviral application that blocked Ebola infectivity across virus strains from multiple epidemics. Atomwise uses the physical or predicted design of a target protein for initial screening via convolutional neural network (CNN) models and draws on data from standard assays to perform counter-screens and narrow the pool of hits for effects like oral bioavailability or blood-brain barrier permeability. The company also performs activities that simulate those real-life activities in surgery, such as cutting simulated tissue and manipulating small objects.(2)

Atomwise, a startup using AI to accelerate drug discovery has secured $123 million in funding this year. It will allow the startup to scale its technology and team as it expands its portfolio of collective experiences with researchers at the University of Toronto, Duke University School of Medicine, and others. Nowadays, fewer than 12% of all drugs entering clinical trials end up in pharmacies. Medicines take at least ten or more years to conclude the journey from discovery to the marketplace.
According to the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America, clinical trials alone take six to seven years, costing production roughly $2.6 billion. Atomwise claims its AtomNet platform can filter 16 billion chemical compounds for probable hits in under two days, expediting a process that typically takes months or years. AtomNet’s AI algorithms screen for strength and the degree to which a pharmaceutical drug acts on a given site while protecting against toxicity, and they work on marks in hard-to-reach parts of the body. In one instance, Atomwise claims it was able to inhibit a protein-protein interaction in the nervous system for a multiple sclerosis project, exploring 8.2 million molecules that were useful in animal trials and have been approved by a pharmaceutical corporation in the UK. In another, the company found a drug candidate with no previous antiviral application that blocked Ebola infectivity across virus strains from multiple epidemics.
Atomwise uses the physical or predicted design of a target protein for initial screening via convolutional neural network (CNN) models and draws on data from standard assays to perform counter-screens and narrow the pool of hits for effects like oral bioavailability or blood-brain barrier permeability. The company also performs activities that simulate those real-life activities in surgery, such as cutting simulated tissue and manipulating small objects.(2)
ClosedLoop AI: Digging into patient data
ClosedLoop was the 1st Place Winner of the AI Health Outcomes Challenge and named Best in KLAS for Healthcare AI: Data Science Solutions in 2022 among 300 entrants in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) with a $1.6 million grant award. ClosedLoop is healthcare’s data science forum, making it easy for healthcare institutions to use AI to improve results and reduce costs. Purpose-built and committed to healthcare, ClosedLoop combines an intuitive end-to-end machine-learning platform with a comprehensive library of healthcare-specific elements and model templates. Clients use ClosedLoop’s Explainable AI to drive clinical excellence, operational efficiency, value-based contracts, and enhanced revenue.

Headquartered in Austin, Texas, ClosedLoop is committed to improving health equity as a core strategic objective of transformative value-based care programs. ClosedLoop is part of the AWS Healthcare Accelerator program, a feature that will help the company to share its healthcare-focused AI/ML platform and content with healthcare organizations throughout the AWS and KidsX networks. This opportunity will allow ClosedLoop to provide services to parties interested in using data to identify and reduce health disparities.(3)
ClosedLoop was the 1st Place Winner of the AI Health Outcomes Challenge and named Best in KLAS for Healthcare AI: Data Science Solutions in 2022 among 300 entrants in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) with a $1.6 million grant award. ClosedLoop is healthcare’s data science forum, making it easy for healthcare institutions to use AI to improve results and reduce costs.

Purpose-built and committed to healthcare, ClosedLoop combines an intuitive end-to-end machine-learning platform with a comprehensive library of healthcare-specific elements and model templates. Clients use ClosedLoop’s Explainable AI to drive clinical excellence, operational efficiency, value-based contracts, and enhanced revenue. Headquartered in Austin, Texas, ClosedLoop is committed to improving health equity as a core strategic objective of transformative value-based care programs. ClosedLoop is part of the AWS Healthcare Accelerator program, a feature that will help the company to share its healthcare-focused AI/ML platform and content with healthcare organizations throughout the AWS and KidsX networks. This opportunity will allow ClosedLoop to provide services to parties interested in using data to identify and reduce health disparities.(3)
First FDA-cleared autonomous AI makes new moves in healthcare diagnostics
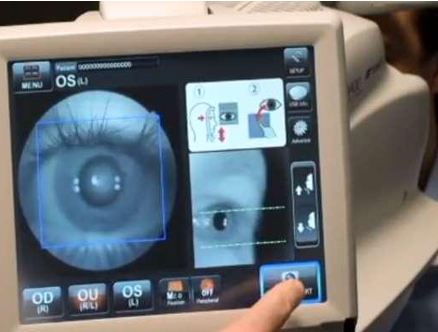
TDigital Diagnostics (formerly known as IDx) is a software enterprise located in Coralville, Iowa, US. It made headlines when it became the first autonomous AI system authorized by the US Food and Drug Administration to use AI technology to autonomously detect diabetic retinopathy in adults with diabetes without needing input from a doctor. Its AI-diagnostic system, the IDX-DR, can identify diabetic retinopathy, one of the most common causes of blindness in the US and other developed countries, and other serious eye diseases, including macular edema. The software starts with several images taken by the Topcon TRC-NW400, a fully automated non-mydriatic retinal camera designed to obtain high-resolution color images of the retina and the anterior component of the eye.
The images are assigned to the AI program electronically, and a result is delivered within minutes, allowing the identification of patients who need a referral to an eye care expert at the time of the visit. It is an attractive choice for practices that struggle to reach the recommended retinopathy screening quality measure.(4)

TDigital Diagnostics (formerly known as IDx) is a software enterprise located in Coralville, Iowa, US. It made headlines when it became the first autonomous AI system authorized by the US Food and Drug Administration to use AI technology to autonomously detect diabetic retinopathy in adults with diabetes without needing input from a doctor.
Its AI-diagnostic system, the IDX-DR, can identify diabetic retinopathy, one of the most common causes of blindness in the US and other developed countries, and other serious eye diseases, including macular edema. The software starts with several images taken by the Topcon TRC-NW400, a fully automated non-mydriatic retinal camera designed to obtain high-resolution color images of the retina and the anterior component of the eye. The images are assigned to the AI program electronically, and a result is delivered within minutes, allowing the identification of patients who need a referral to an eye care expert at the time of the visit. It is an attractive choice for practices that struggle to reach the recommended retinopathy screening quality measure.(4)
AI-powered imaging to analyze heart scans
Cleerly, a New York City-based healthcare startup focused on employing artificial intelligence (AI) to assess plaque buildup in cardiac CT findings, has closed a financing round worth $192 million. The Fierce 15 winner’s technology aims to catch potentially fatal heart disease well before symptoms arise, mainly since a heart attack is the first indicator of coronary artery disease for many patients. Cleerly’s machine learning AI evaluates noninvasive CT angiography scans of the heart to describe and measure the amount of plaque built up in the arteries. By assessing the likelihood of buildups causing total blockage of oxygen supply to a patient’s heart, the software can identify early signs of heart disease and calculate the risk that a patient will experience a heart attack.
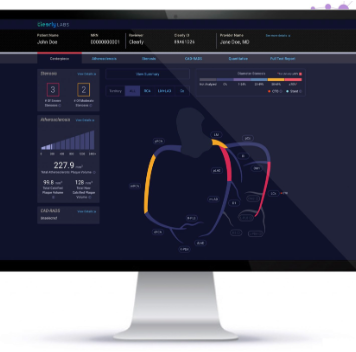
The system is powered by a database of millions of previously assessed CT images and data collected in clinical trials spanning thousands of patients. Cleerly aspires to further expand that repository with its ongoing analyses, which plan to enroll more than 100,000 patients from across the globe within the next decade. In the study, led by researchers from the George Washington University School of Medicine, the AI’s research went head to head with angiography for quantitative coronary angiography in detecting and grading the severity of a narrowed coronary artery. The AI produced analyses of the blockages with 94% sensitivity and between 68% and 82% specificity, depending on the severity of the stenosis. The AI’s assessments resulted in accuracy levels of at least 84% and showed a strong correlation.(5)
Cleerly, a New York City-based healthcare startup focused on employing artificial intelligence (AI) to assess plaque buildup in cardiac CT findings, has closed a financing round worth $192 million. The Fierce 15 winner’s technology aims to catch potentially fatal heart disease well before symptoms arise, mainly since a heart attack is the first indicator of coronary artery disease for many patients.

Cleerly’s machine learning AI evaluates noninvasive CT angiography scans of the heart to describe and measure the amount of plaque built up in the arteries. By assessing the likelihood of buildups causing total blockage of oxygen supply to a patient’s heart, the software can identify early signs of heart disease and calculate the risk that a patient will experience a heart attack. The system is powered by a database of millions of previously assessed CT images and data collected in clinical trials spanning thousands of patients. Cleerly aspires to further expand that repository with its ongoing analyses, which plan to enroll more than 100,000 patients from across the globe within the next decade.
In the study, led by researchers from the George Washington University School of Medicine, the AI’s research went head to head with angiography for quantitative coronary angiography in detecting and grading the severity of a narrowed coronary artery. The AI produced analyses of the blockages with 94% sensitivity and between 68% and 82% specificity, depending on the severity of the stenosis. The AI’s assessments resulted in accuracy levels of at least 84% and showed a strong correlation.(5)
Owkin: Finding the right drug for every patient

Owkin, a French-American startup, was founded by Thomas Clozel, MD, a clinical research doctor and former assistant professor in clinical onco-hematology, and Gilles Wainrib, a pioneer in machine learning in biology, in 2016. It now works with the most renowned cancer centers and biopharma companies in Europe and the US. Owkin uses artificial intelligence to discover the proper treatment for every patient. The software uses AI to identify new drug candidates and risks, accelerate clinical trials, and build diagnostic tools that improve patient outcomes. Owkin unlocks valuable insights from siloed datasets using federated learning while protecting patient privacy and securing proprietary data. AI-based diagnostic solutions designed to improve outcomes for patients with breast and colorectal cancer have been approved in Europe.
Using AI to analyze digital pathology images is designed to help clinicians make precision medicine more accessible to patients at an earlier stage of their disease. Owkin has become the first approved digital pathology-based AI diagnostic that predicts early breast cancer patients’ relapse risk.(6)

Owkin, a French-American startup, was founded by Thomas Clozel, MD, a clinical research doctor and former assistant professor in clinical onco-hematology, and Gilles Wainrib, a pioneer in machine learning in biology, in 2016. It now works with the most renowned cancer centers and biopharma companies in Europe and the US. Owkin uses artificial intelligence to discover the proper treatment for every patient.
The software uses AI to identify new drug candidates and risks, accelerate clinical trials, and build diagnostic tools that improve patient outcomes. Owkin unlocks valuable insights from siloed datasets using federated learning while protecting patient privacy and securing proprietary data. AI-based diagnostic solutions designed to improve outcomes for patients with breast and colorectal cancer have been approved in Europe.Using AI to analyze digital pathology images is designed to help clinicians make precision medicine more accessible to patients at an earlier stage of their disease. Owkin has become the first approved digital pathology-based AI diagnostic that predicts early breast cancer patients’ relapse risk.(6)
Deepcell: AI for a new cell biology research
Founded in 2017, Menlo Park, California-based Deepcell, designed at Stanford University, raised fresh funds to use artificial intelligence to find new ways to understand biology. The group has developed unique microfluidics-based technology that uses continuous learning AI to classify cells based on detailed visual elements and sort them without innate bias. The Deepcell platform maintains cell viability for downstream single-cell analysis. It can separate virtually any cell at frequencies as low as one billion. The technology will initially be a translational research, diagnostics, and therapeutic development service.(7)
Founded in 2017, Menlo Park, California-based Deepcell, designed at Stanford University, raised fresh funds to use artificial intelligence to find new ways to understand biology. The group has developed unique microfluidics-based technology that uses continuous learning AI to classify cells based on detailed visual elements and sort them without innate bias.

The Deepcell platform maintains cell viability for downstream single-cell analysis. It can separate virtually any cell at frequencies as low as one billion. The technology will initially be a translational research, diagnostics, and therapeutic development service.(7)
