2019-2020 “Revolutionizing Gastroenterology: The Emergence of Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Procedures”
January 31, 2024PerClot: A Breakthrough in Surgical Hemostasis
January 31, 2024AI Cure
Overview
AiCure is a data analytics firm that uses artificial intelligence to understand better how patients react to treatments. As a result, it allows for more informed decision-making and better health results. It has proprietary facial recognition and motion-sensing technology that certifies drug consumption in real time. By improving treatment and lowering hazards, this platform can transform the cost-effectiveness of healthcare delivery systems. Their software gathers and interprets video, audio, and behavioral data to establish the relationship between patients, disease, and therapy. These insights from their AI platform assist areas that better serve patients and sponsors by helping them create the correct study for the right patient, resulting in improved medication efficacy information, faster timelines, and lower trial costs and variability.
The Appropriate Dose for the Right Patient
AiCure provides a scalable, compliant AI platform that enhances clinical research data and operations from pre-clinical through commercialization. This company uses AI to help data-driven decision-making within the life sciences industry, leading to more relevant clinical trials, better medication development, and enhanced company operations.(1)
AiCure Patient ConnectTM is a mobile application with a suite of HIPAA and GDPR-compliant capabilities to increase patient involvement, strengthen the site-patient connection, and get a more profound knowledge of individual and population-wide illness symptomology for better health and trial results.(2)
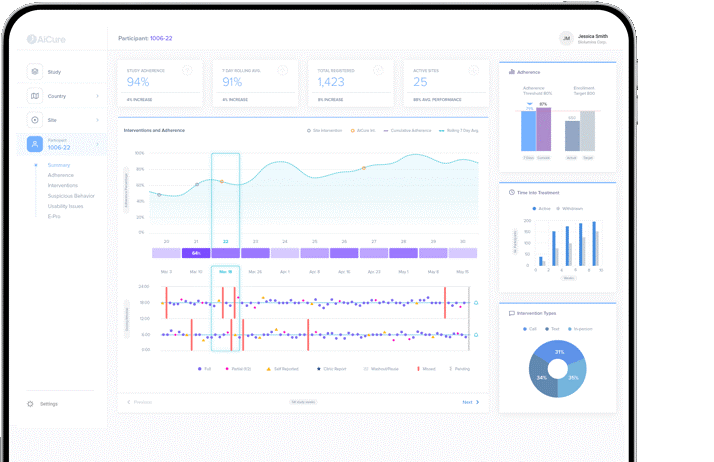
AiCure Data Intelligence is the company’s next-generation data dashboard, which provides sponsors with improved visibility into the success of each trial through a single, holistic data center. The dashboards provide quick assessments of trial and site performance, patient dose and symptoms, intervention resolution percentages, and more – all of which feed solid predictive analytics and aid proactive data-driven decision-making. In addition, it is built with extensive configurability in mind, allowing sponsors to analyze various data views based on their needs.(3)

All types of trials may be supported, from traditional site-based to decentralized or virtual trials. Data acquired through AiCure’s secure, patient-facing application can help with safety and effectiveness objectives and give a holistic picture of how therapy affects patients. In addition, AiCure supports a wide range of trials, including standard site-based trials and site-less, decentralized, or virtual trials.(4)
AiCure’s AI platform as a service (PaaS) allows collecting data from diverse sources to correlate unconnected endpoints and turn them into meaningful and actionable insights that can be deployed at scale. Consequently, life sciences companies may use the platform in various ways to understand research parameters better and make business decisions that will help them optimize and speed up the creation of high-quality medications.
AiCure Builds Open-source Code to Improve Digital Biomarker Development
OpenDBM is an open-source platform that allows scientists to use AiCure’s digital biomarker algorithms and apply them to their own data sets to assess patient behavior, foster research cooperation, and improve illness symptomatology knowledge. It combines current techniques for measuring behavioral traits, including face activity, speech, and movement, into a single package for total behavior measurement. In addition, it is created to be simple to use, making such technologies more accessible to the scientific community.(5)
Using an Artificial Intelligence Platform on Mobile Devices to Monitor and Increase Adherence in Subjects with Schizophrenia
The use and adherence to medication in the treatment of schizophrenia are considered fundamental for the management of the disease. The study aimed to establish the importance of ensuring optimal adherence in clinical trials, especially in ambulatory patients.
Researchers evaluated an AI system as a real-time monitoring method for adherence to antipsychotics and the possibility of applying the platform to increase adherence and retention in the clinical trial for patients with negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
For the study, patients were randomly assigned to one of the six treatment sequences; each received a three-week treatment course. Every treatment period was separated by a washout time of fourteen days. The AI system was downloaded to smartphones and used every time medication was administered.
Results showed that the mean cumulative dose adherence and scheduled pill counts were 95% and 99.7%, respectively. The study shows the potential for using AI systems to improve adherence and, on the other hand, detect nonadherence. (6)

Using Computer Vision and Machine Learning to Identify Patterns of Fraudulent Participant Activity in CNS Trials

In clinical trials, participant dosing is usually measured through unreliable methods, including pill counts and self-reports. Even though discrepancies have been detected, including differences between pharmacokinetics data and pill counts, real-time evidence of misuse has not been registered yet.
This study used an AI system (composed of computer vision and ML for visual detection) in seven different CNS trials to monitor drug administration and adherence. Patients are given smartphones with the AI system installed and asked to use the application whenever they take their medications. The system registered logging adherence parameters and visual misuse of the platform.
Results showed a total of 102 participants misusing the platform. The fraudulent behaviors included obstructing the view of the mouth, spitting out the drug, “cheeking,” leaning out of the field of view, and presenting something different to the study drug.(7)
AI Platform Could Evaluate Schizophrenia Treatment Adherences
A total of 92 patients were included in a double-blinded placebo treatment and subsequently followed a “try-out phase” placebo phase. The patients were asked to monitor their drug compliance using an AI smartphone application. The results revealed that AI usage identified 98% of people who correctly adhered to their treatment. This suggests that the non-compliance rate was minimal.
Precise drug adherence monitoring offers us insight into possible drug effects and can increase the quality of the collected data.(8)

AI Platform Used to Increase Medical Adherence

164 subjects were asked to monitor their drug administration through an AI platform application downloaded on their smartphone. The adherence measures were based on pill number, AI platform adherence, and pharmacodynamic data. Results were encouraging and revealed that the cumulative adherence based on pill count ranged from 95% to 100%.
AI platforms could be used to detect non-compliance and predict future nonadherence in CNS trials. It can also lead to a better understanding of clarification of clinical trial outcomes.(9)
